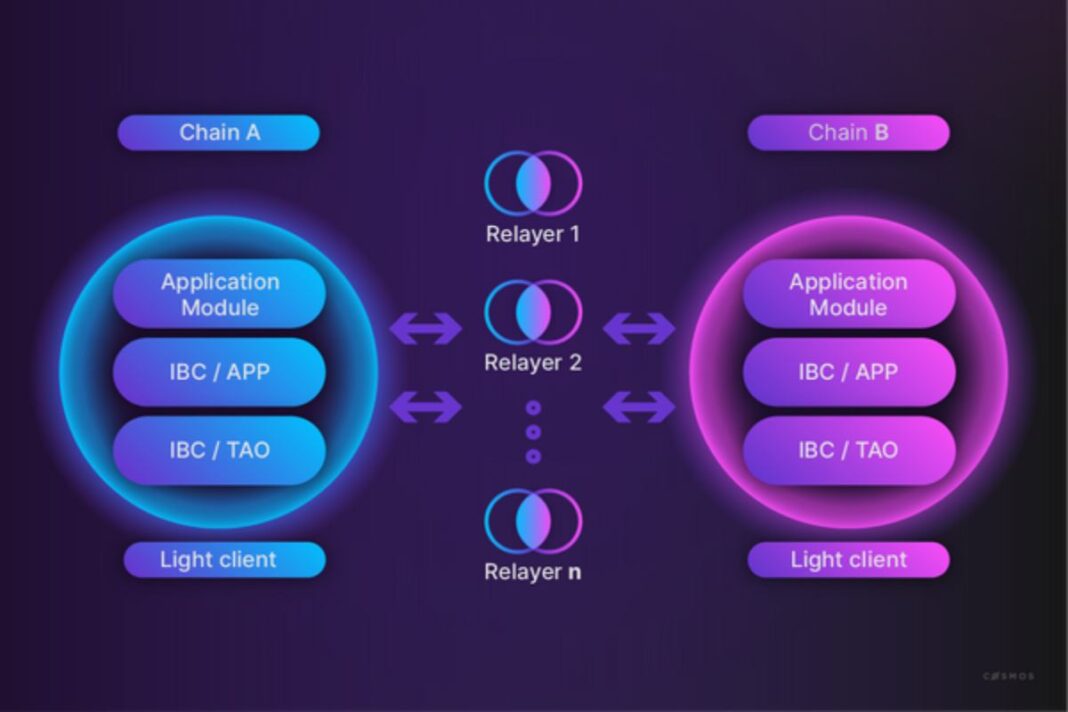
Inter-blockchain communication (IBC) is at the core of blockchain interoperability. It allows different blockchains to exchange data and assets smoothly. IBC relayers are off-chain processes that connect these networks by passing data packets between them. In this article, we break the process down into five key points: understanding IBC relayers, setting up your environment, configuring and deploying the relayer, optimizing performance, and monitoring plus scaling your deployment.
1. Understanding IBC and the Role of Relayers
Before diving into the technical setup, it is important to understand the basics of IBC and the relayer’s role. The IBC protocol securely transfers data and tokens between different blockchains by creating trusted channels, connections, and light clients. Relayers act as middlemen who watch blockchains for outgoing IBC packets. They then submit these packets along with proofs to the destination chain.
Popular IBC relayer tools—like Hermes, built with Rust, and the Go Relayer—offer command-line tools for relaying transactions and tracking performance. Knowing these concepts helps you see how efficient relaying enables smooth cross-chain transfers. It also ensures blockchains stay interoperable without losing security or decentralization.
2. Setting Up Your Environment
Next, prepare your setup for deploying an IBC relayer. This means meeting system needs, installing necessary software, and getting access to both source and destination blockchain nodes. Key requirements include:
-
Operating System and Hardware: Use a Linux server with enough CPU, RAM, and storage to handle blockchain queries and relayer tasks.
-
Programming Tools: For example, if using Hermes, install Rust (version 1.65 or higher).
-
Blockchain Nodes and Endpoints: Run or connect to full nodes for all blockchains you want to link. Configure RPC, gRPC, and WebSocket endpoints.
-
Wallets and Keys: Have secure wallet seed phrases and keys for each chain to pay for transactions and gas fees when relaying messages.
With these in place, you set a strong base for smooth relayer setup.
3. Configuring and Deploying Your IBC Relayer
Once ready, install and configure your relayer. Using Hermes as an example:
Installation:
Clone the official repo (e.g., from Informal Systems for Hermes) and check out the latest stable version. Then build the project with Cargo:
git clone https://github.com/informalsystems/ibc-rs.git
cd ibc-rs/relayer-cli
git checkout v1.4.1 # change if needed
cargo build --release
Setting Up Wallets:
Add wallet keys for each blockchain via relayer commands:
hermes keys add --chain chain-id --mnemonic-file ./your-wallet.seed
Editing Config File:
Create or update the config file (usually config.toml) with chain endpoints (RPC, gRPC, WebSocket), gas price, packet filters, and relayer modes (channels, connections, packet relay).
Deployment:
Start the relayer with:
hermes start --config=config.toml
A well-set config keeps the relayer communicating efficiently and securely.
Optimizing Relayer Performance
After deploying, focus on improving your relayer’s performance with these tips:
-
Parameter Tuning:
Adjust settings likeclear_interval(how often relayer checks packets) andtx_confirmation. Shorter intervals reduce delay but increase server load. Find a balanced setting. -
Network Optimization:
Keep low network latency between relayer and blockchain nodes. Use strong connectivity or co-locate nodes and relayer on the same server or cloud zone. -
Gas Price and Fee Management:
Set gas prices smartly to avoid failed transactions and ensure validators process packets quickly. Monitor fees and adjust to prevent overpaying while keeping speed. -
Batching and RPC Optimization:
Relayers can be slowed by checking RPC queries one by one. Batch queries or configure nodes to allow parallel requests to reduce total relay time.
Applying these steps helps your relayer run efficiently, reduces delays, and makes cross-chain transfers more reliable.
Monitoring and Scaling Your Relayer Deployment
Maintaining your relayer requires constant monitoring and scaling:
-
Telemetry and Logging:
Use tools like Prometheus and Grafana to track performance metrics (speed, errors, throughput) in real-time. -
Error Handling and Alerts:
Set automatic alerts for errors like many failed transactions or increased delays. Fast detection allows quick fixes. -
Scaling:
If traffic grows, deploy multiple relayers. Coordinate them to avoid duplicate efforts or redundant packets. Future protocol updates may improve this coordination. -
Regular Maintenance and Updates:
Keep relayer software and blockchain nodes updated to fix bugs, improve performance, and enhance security.
Good monitoring and scaling protect your relayer’s uptime and support a robust IBC infrastructure.
Conclusion
Setting up and improving an IBC relayer includes multiple steps. Start by understanding its role in the larger IBC system, prepare your environment, and deploy the relayer with a solid plan. Then optimize by tuning settings, managing network and gas fees. Finally, monitor closely and scale your deployment as needed. Following these five main steps helps blockchain developers ensure reliable and effective cross-chain communication while unlocking blockchain interoperability’s full potential.
Check Out: eod-adventure-park-photos